See brilliantly
Cataracts in
a perspective
-
A Normal Part of Aging
Most people over 65 will develop cataracts.
-
You Have Options
You have an important choice to make when it comes to the kind of vision you want after cataract surgery.
-
Highly Successful Surgery
Cataract surgery is one of the most successful surgical procedures of all time.
-
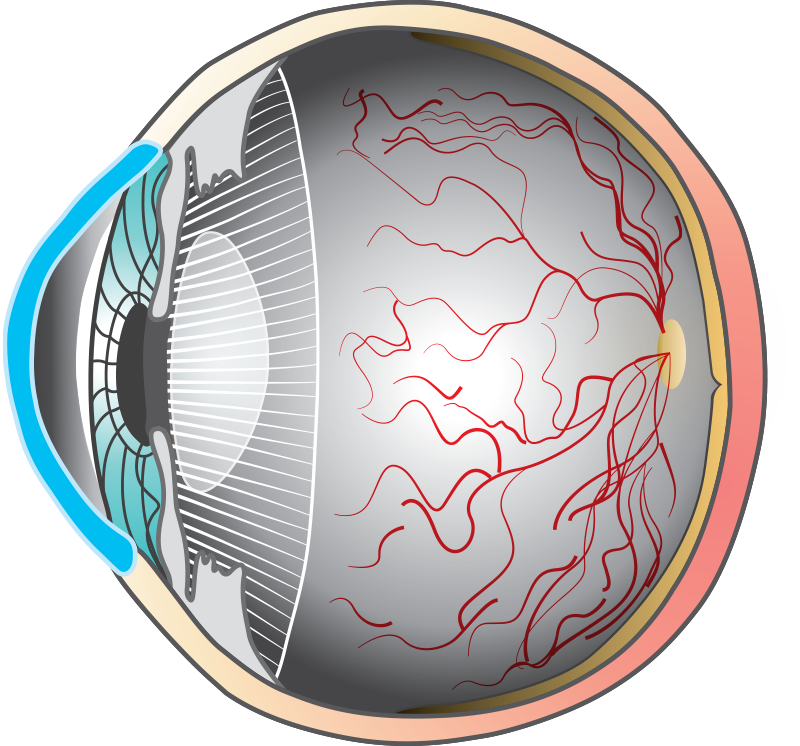
What is Cataracts?
Yellowing of the natural lens that may block you from seeing clearly.
-
Treatment
Removed with a safe, common outpatient surgery and replaced with a small, soft intraocular lens (IOL).
-
Age 60+
Very common and usually become noticeable after age 60*.
Have you been
diagnosed
with cataracts?
Understanding other
eye conditions
ASTIGMATISM is a common defect in the shape of a cornea that blurs vision and distorts light before it reaches the lens of the eye. If you have astigmatism but don’t get it corrected during cataract correction, you may still need to wear glasses after the procedure.

ASTIGMATISM is a common defect in the shape of a cornea that blurs vision and distorts light before it reaches the lens of the eye. If you have astigmatism but don’t get it corrected during cataract correction, you may still need to wear glasses after the procedure.


Blurry vision
Glare
Double vision
Change in colours
Second sight
In this situation, the cataract acts as a stronger lens, temporarily improving the ability to see things at a close distance. People who formerly needed reading glasses may no longer need them However, as the cataract worsens over time, this temporary improvement in near vision disappears.
New prescriptions
4 stages of cataract
development.
- THE EARLY STAGE
- THE IMMATURE STAGE
- THE MATURE STAGE
- THE HYPER-MATURE STAGE
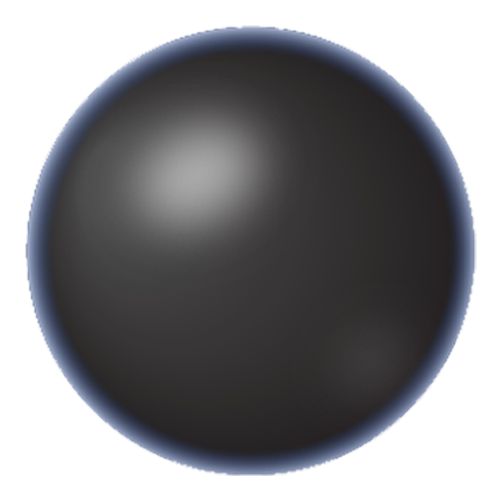

The Early Stage
Symptoms
-
Mild burning or clouding
-
Increasing eye strain
-
Increasing light sensitivity
-
Early appearance of glare
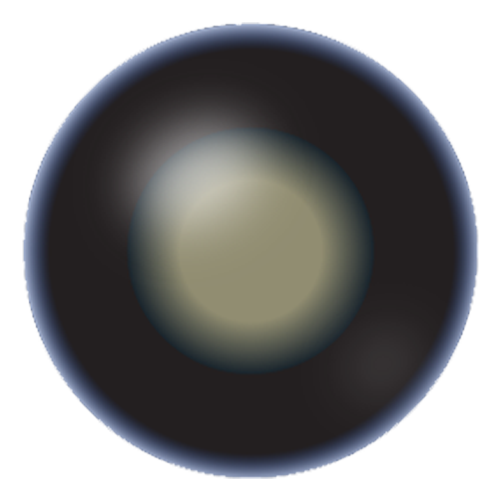

The Immature Stage
Symptoms
-
Blurred vision
-
Dimmed vision
-
Double vision
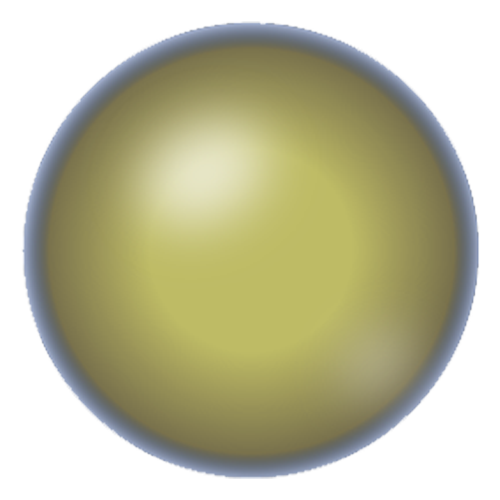

The Mature Stage
Symptoms
-
Blurred vision
-
Dimmed vision
-
Double vision
-
Difficulty in seeing things, altering quality of life
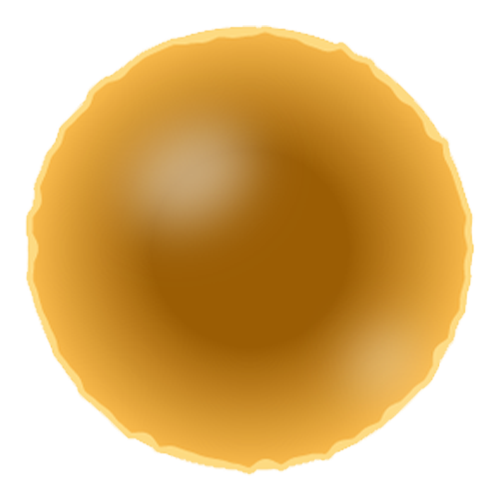

The Hyper-mature Stage
Symptoms
-
Loss of vision
-
Significant blur
-
Double vision
Types of
Cataract
The progression rate varies depending on the type
of cataract you have been diagnosed with.2

Nuclear Sclerotic
These cataracts form deep in the nucleus. The yellowing and hardening of the central portion of the crystalline lens occurs slowly over years.

Cortical
These Cataract have white opaque "spoke" that start peripheral vision and works toward the center. Progression is variable with some progressing over years and others in months.

Posterior Subcapsular
Progression is variable but tends to progress more rapidly than nuclear sclerotic cataracts. They affect diabetics and people who use high doses of steroids.
Early treatment
is the key
Depending on the IOL you choose (in conjunction with your surgeon), cataract surgery may also help you become less dependent on glasses, or even spectacle-free.
It’s important to discuss your IOL options with your surgeon prior to surgery to ensure you receive the IOL most suited to your needs.2
Find a cataract surgeon
near you
locate a surgeon near you who offers
a range of IOL options.
Download our
discussion guide
your doctor to understand the IOL choice
that;s right for you.
References
- Cataract. Kellogg Eye Center website. https://www.umkelloggeye.org/conditions-treatments/cataract. Accessed Feb 09, 2023.
- https://www.sweye.com/blog/cataracts/cataract-progression-rate/
- https://www.medicinenet.com/cataracts_pictures_slideshow/article.htm
- Please refer to the relevant product operator’s manual for a complex list of indications, contradictions, and warnings.

The Early Stage
At this stage, the lens remains clear but the ability to focus at distance and then refocus on near objects is slowly lost.
Symptoms
-
Mild burning or clouding
-
Increasing eye strain
-
Increasing light sensitivity
-
Early appearance of glare

The Immature Stage
At this stage, lens opacity is enough to noticeably obstruct vision. If the eye is illuminated from the side, the edge of the pupil casts a shadow on the lens.
Symptoms
-
Blurred vision
-
Dimmed vision
-
Double vision

The Mature Stage
A mature cataract causes the lens to become completely white or deep amber in colour. The iris edge no longer casts a shadow.
Symptoms
-
Blurred vision
-
Dimmed vision
-
Double vision
-
Difficulty in seeing things, altering quality of life

The Hyper-mature Stage
At this stage, the lens becomes shrunken with white spots and occasionally may partially dislocate or suffer from secondary glaucoma.
Symptoms
-
Loss of vision
-
Significant blur
-
Double vision

